Overview
ZKsync Connect enables interoperability across ZKsync chains in the Elastic Network. Interop, or interoperability, is a way to communicate and transact between two ZK Stack chains. It is made possible by smart contracts that verify transactions across chains using Merkle proofs.
It allows you to:
- Observe messages: Track when an interop message (think of it as a special event) is created on the source chain.
- Send assets: Transfer ERC20 tokens and other assets between chains.
- Execute calls: Call a contract on a remote chain with specific calldata and value.
With interop, you automatically get an account (a.k.a.
aliasedAccount) on each chain, which you can control from the source chain. - Execute bundles of calls: Group multiple remote calls into a single bundle, ensuring all of them execute at once.
- Execute transactions: Create transactions on the source chain, which will automatically get executed on the destination chain, with options to choose from various cross-chain Paymaster solutions to handle gas fees.
Enhanced user experience
Interoperability enhances the blockchain user experience by abstracting complex cross-chain interactions. Users do not need to manually bridge funds to another chain in the Elastic Network if they already have funds on one.
- Reduced Complexity: Users interact with a seamless interface that hides the underlying complexities of blockchain operations.
- Asset Bridging: Relayers manage the process of bridging assets between chains, handling the necessary burning and minting of assets as they move across the ecosystem.
- Lower Fees: By leveraging efficient relayers and minimizing manual operations, transaction costs are kept low, akin to standard gas fees within a single chain.
Real-World Application: Crosschain Transactions
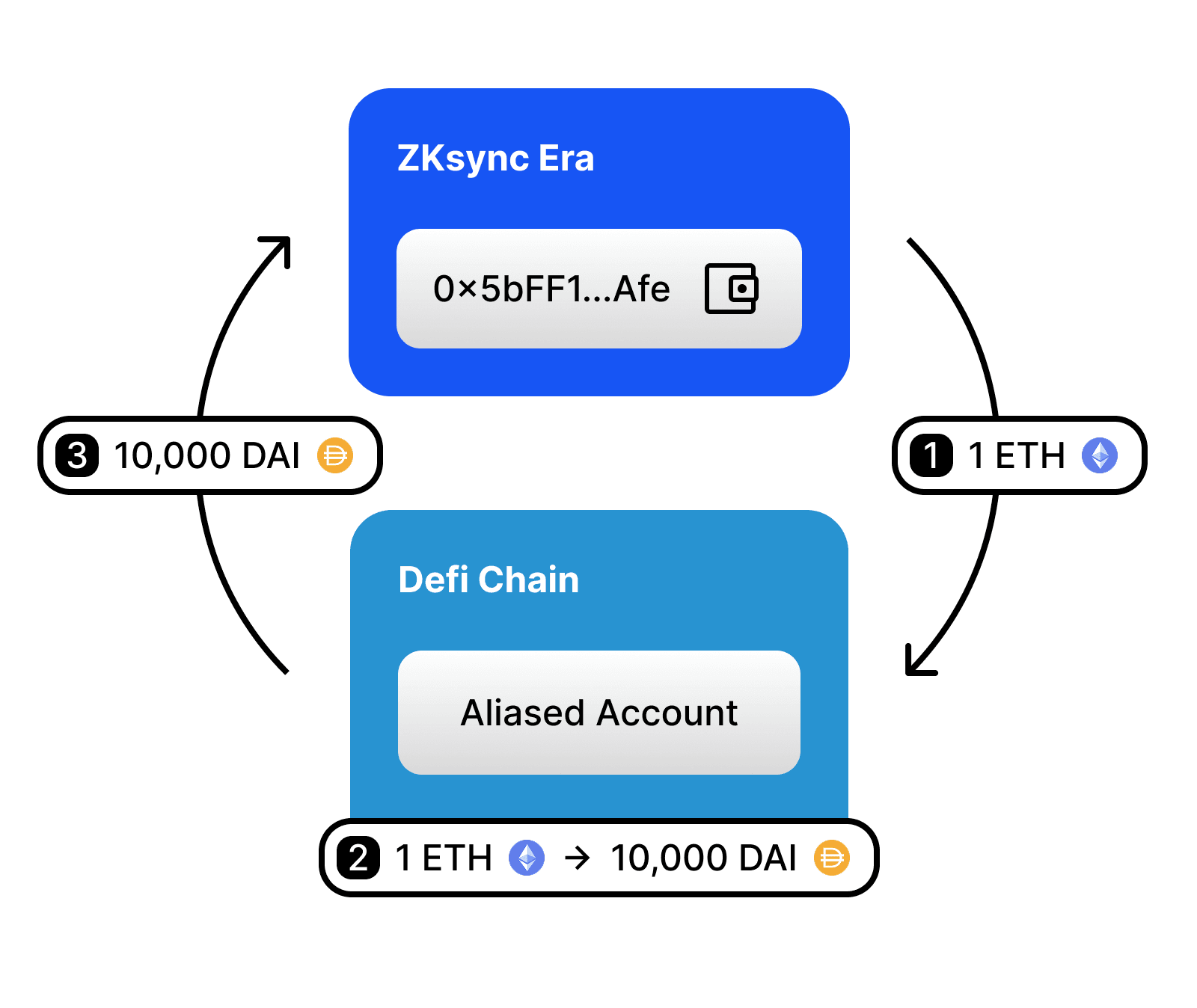
Consider a practical scenario where you want to swap ETH for DAI using a crosschain transaction on a defi platform:
- Transaction Initiation: You initiate the transaction directly from your wallet.
- Relayer Involvement: A relayer picks up your ETH and deposits it into the defi chain.
- Asset Swap: On the defi chain, your ETH is automatically swapped for DAI.
- Completion and Return: The relayer then transfers the DAI back to your original chain.
This entire process is executed as a single transaction, making it feel as seamless as if no chain-switching occurred. The only difference a user might notice is a slightly longer confirmation time, depending on the specific ZKsync chain used.
Transaction Lifecycle
An interop transaction in the Elastic Network follows these steps:
- Initiation: A transaction is initiated on a ZKsync chain, aimed at crossing to another chain within the Elastic Network.
- Settlement on L1: The sending ZKsync chain compiles a cryptographic proof of the transaction and settles it onto Ethereum's Layer 1, anchoring the transaction's validity.
- Transaction Root Update: Ethereum's Layer 1 updates the Transaction Root, a cumulative record reflecting all transactions processed across the Elastic Network.
- Root Importation: The receiving ZKsync chain imports this updated Transaction Root through its consensus mechanism, akin to the way Layer 1 to Layer 2 messages are currently handled.
- Transaction Submission: A relayer submits the transaction along with a Merkle Proof to the receiving ZKsync chain. This proof connects the transaction to the newly updated Transaction Root.
- Verification and Execution: The receiving ZKsync chain verifies the transaction against the Transaction Root. If the verification is successful, the transaction is executed, and the relayer is compensated for their service.
- Proof Settlement: Finally, the receiving ZKsync chain settles its proof on L1, conclusively validating the transaction within the Elastic Network.
Rollout Phases
There are three steps planned for rolling out full interoperability:
- Messaging
- Asset transfers and bundles
- Crosschain transactions
Currently only messaging is available as a part of the v29 upgrade.
Only chains that settle on top of Gateway have access to interop messaging.
To see which chains use ZKsync Gateway, check the Elastic Network Chains table.
Limitations for this first state of interop include:
- No support for selecting destination chains
- Lack of nullifiers or replay protection
- No cancellation mechanism
- No support for sending assets or calling contracts
These limitations will be addressed in steps 2 and 3 of full universal interoperability.