Deploy your first contract
This tutorial shows you how to deploy and interact with a smart contract on ZKsync Era in less than 5 minutes. It will help you get familiar with the ZKsync smart contract development and deployment process using different tools.
In this section you will learn how to:
Build a smart contract to exchange messages with Zeek.
Deploy the smart contract to the ZKsync Sepolia Testnet.
Interact with the contract from your browser using Remix.
Prerequisites
- Before you start, make sure that you’ve configured the ZKsync Sepolia Testnet in your wallet.
- Have at least 0.05 ZKsync Sepolia Testnet ETH. If you need more, use one of the faucets.
Review the smart contract code
The smart contract will store messages from users and emit events with replies from Zeek. The entire code is as follows:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract ZeekMessages {
string[] private messages;
// Event to acknowledge a new message
event MessageReceived(string);
constructor() {
// Zeek initializes the contract with a welcome message
emit MessageReceived("Zeek welcomes you to ZKsync!");
}
function sendMessage(string memory _message) public {
messages.push(_message);
// Acknowledge the message receipt with Zeek's reply
emit MessageReceived("ZK is the endgame - Message received!");
}
// Function to count the total messages sent to Zeek
function getTotalMessages() public view returns (uint) {
return messages.length;
}
// Function to return the last message sent to Zeek
function getLastMessage() public view returns (string memory) {
require(messages.length > 0, "No messages sent to Zeek yet!");
return messages[messages.length - 1];
}
}
The Solidity smart contract contains three functions:
sendMessagestores the messages sent by users in themessagesstate variable.getTotalMessagesreturns the number of messages stored in the smart contract.getLastMessagereturns the last message sent.
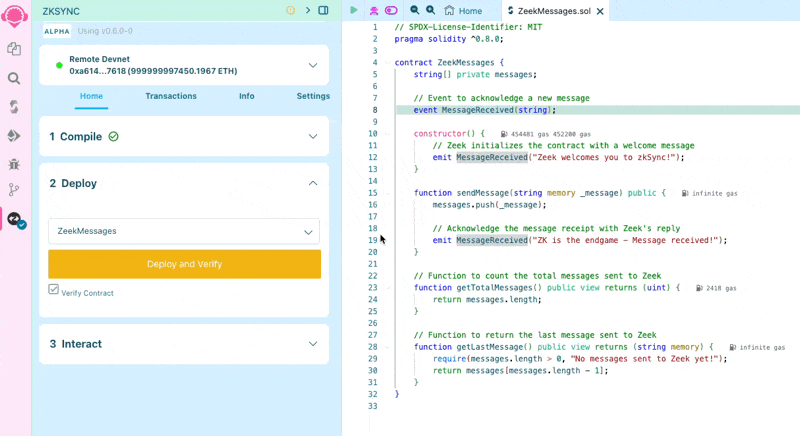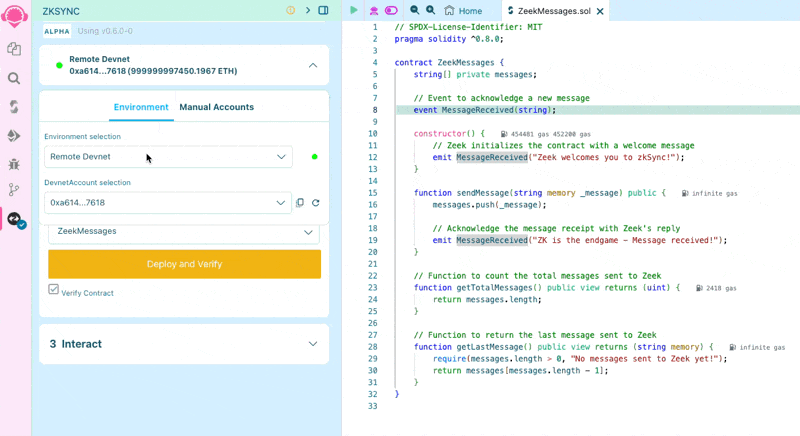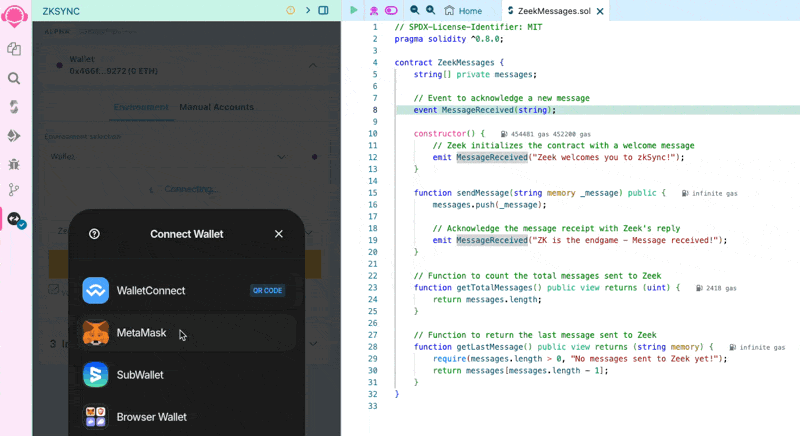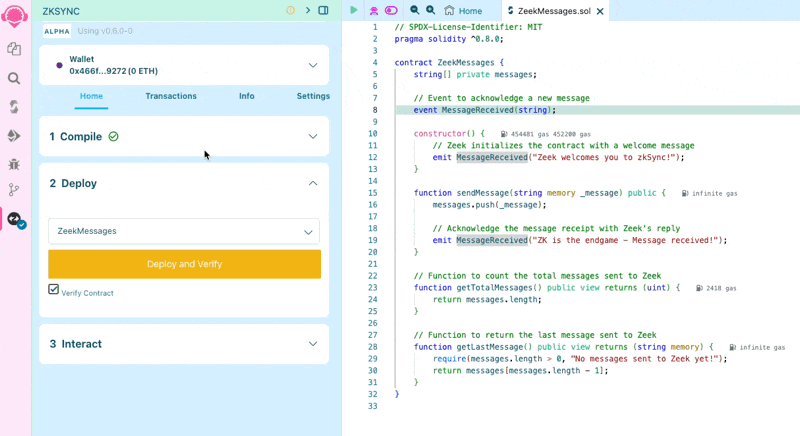
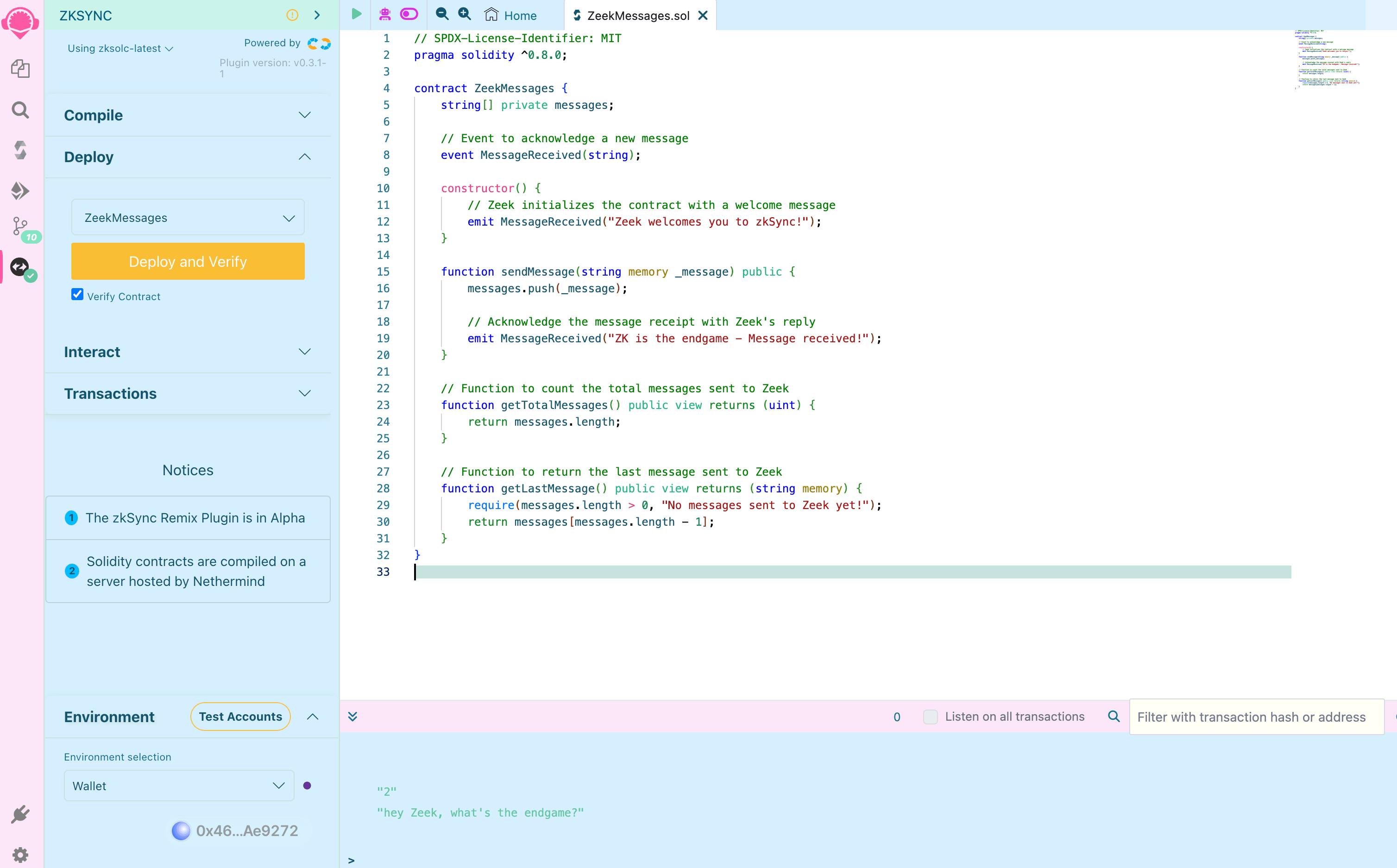
Compile and deploy the contract
To compile and deploy the contract you can use either EVM or EraVM bytecode:
The Remix IDE is an open-source web and desktop application that supports Ethereum smart contract development and deployment, offering tools for writing, testing, debugging, and deploying smart contracts written in Solidity to EVM compatible protocols.
Clone the template project into Remix by clicking the "Clone" button on the "Home" tab under "Files". Then enter the repository URL below:
https://github.com/zkSync-Community-Hub/zksync-quickstart-remix.git
Then, open up the ZeekMessages.sol contract file.
Connect your wallet
On the left side menu bar, select the "Deploy & Run Transactions" tab. Click on the "Environment" dropdown menu, select "Customize this list...". Then, click the toggle icon to enable an injected wallet provider.
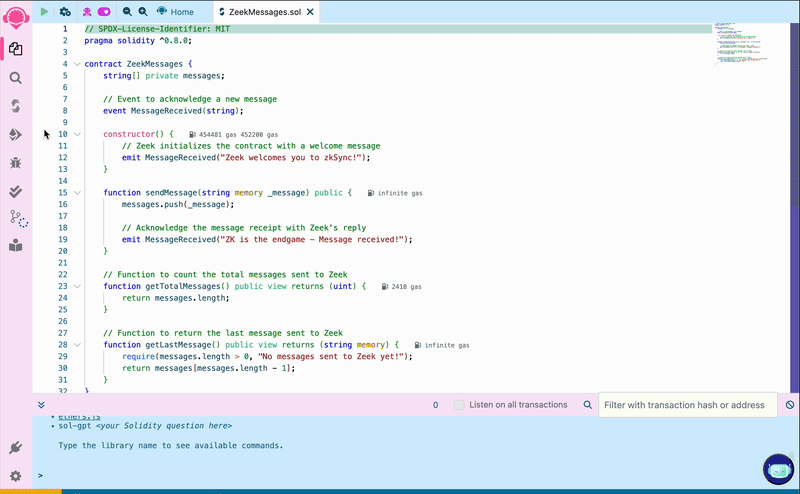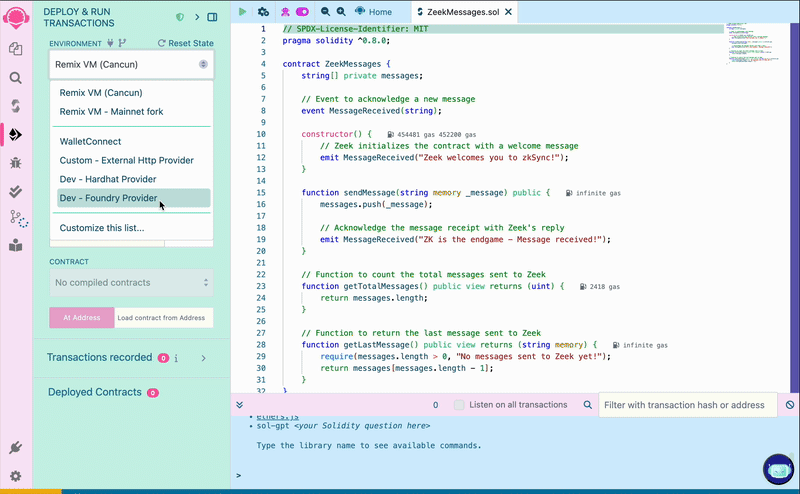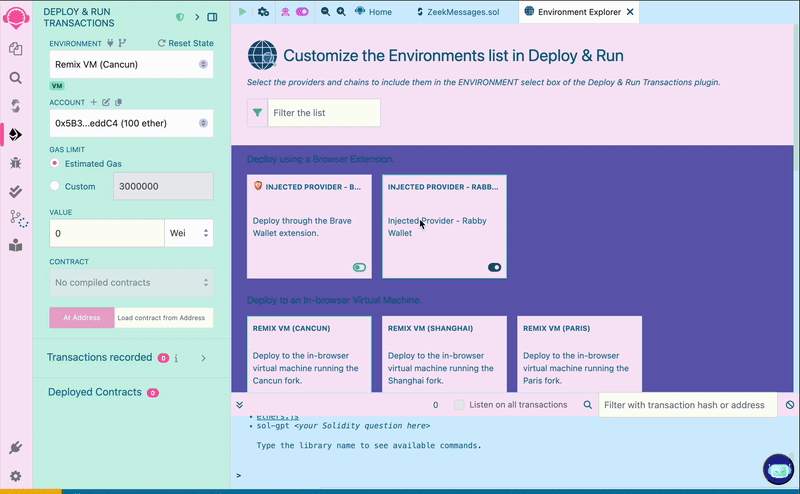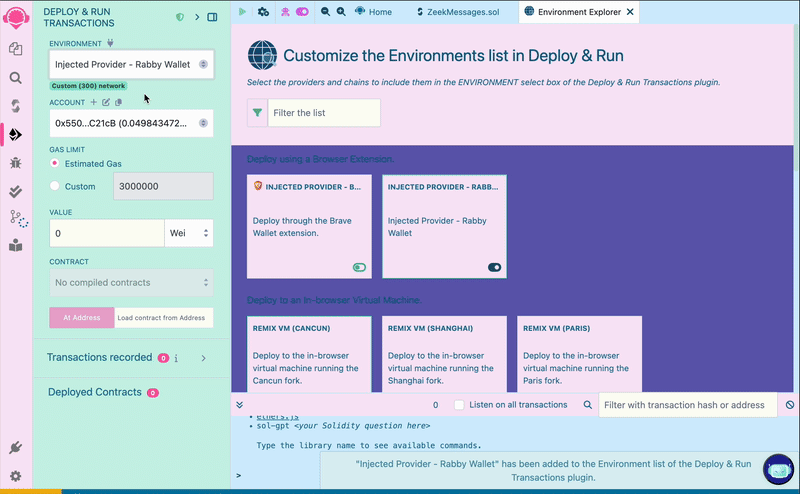
Make sure your wallet is currently connected to the ZKsync Sepolia Testnet, as we will use our wallet’s configured network to deploy our smart contract.
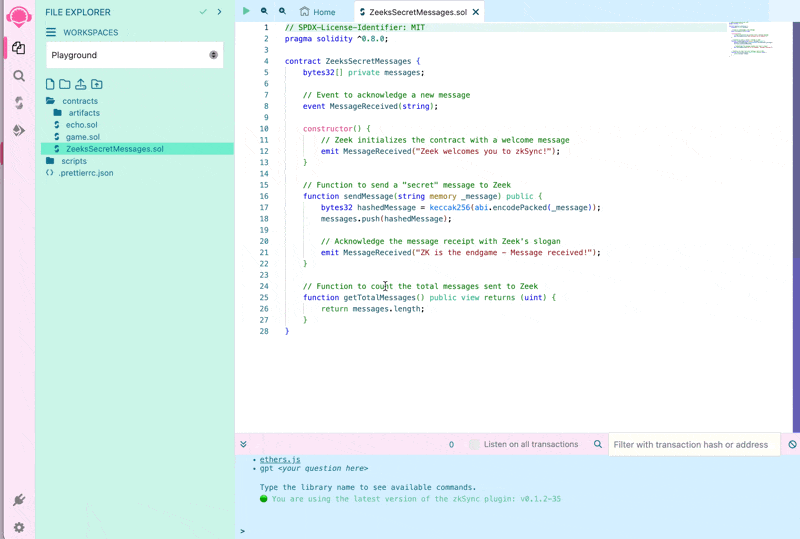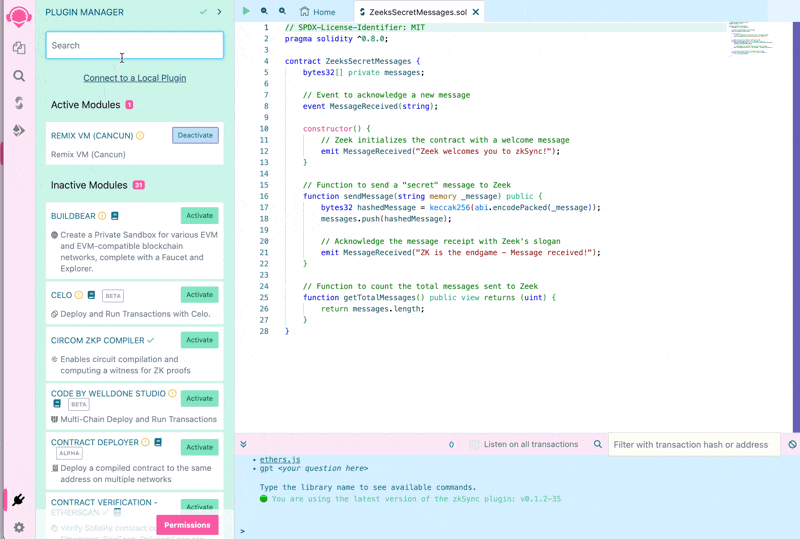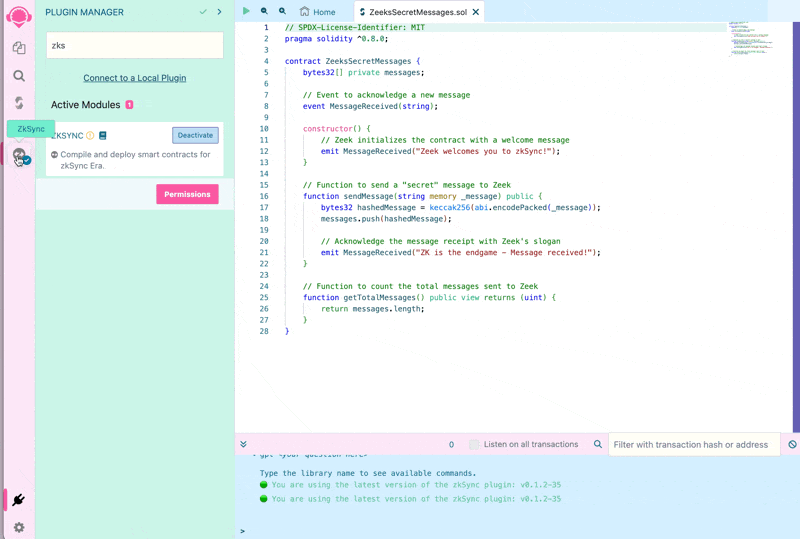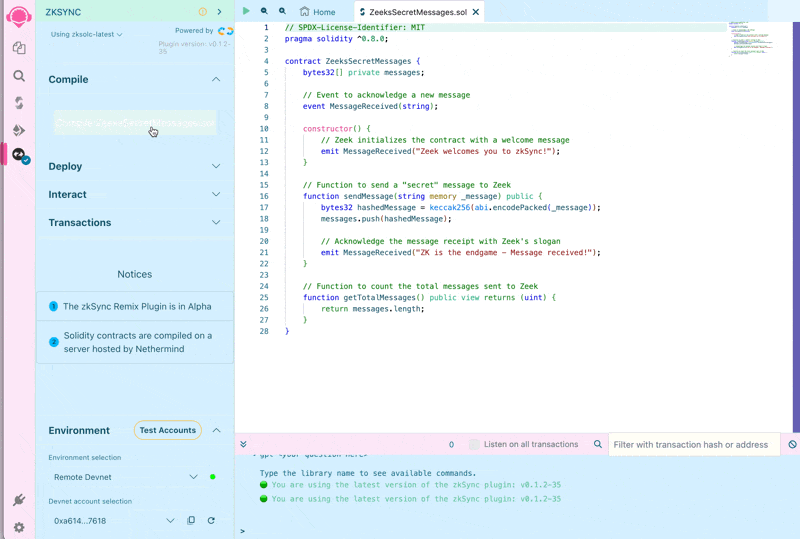
Compile the contract
To compile the contract, click on the "Solidity Compiler" tab and press the "Compile ZeekMessages.sol" button.
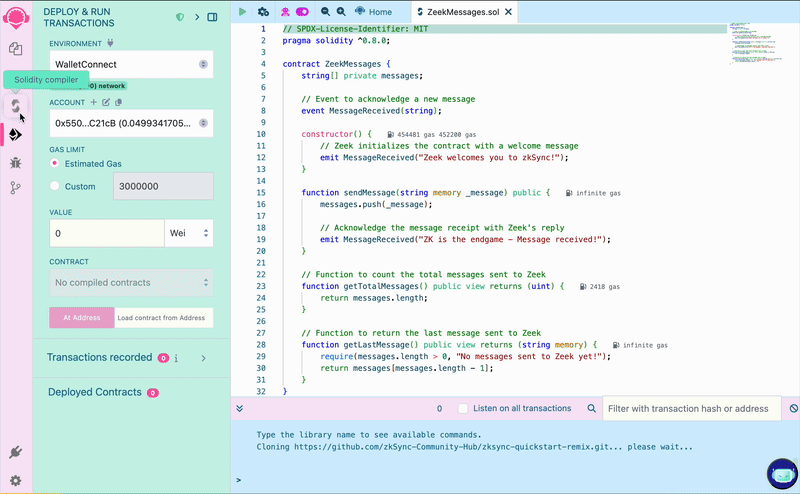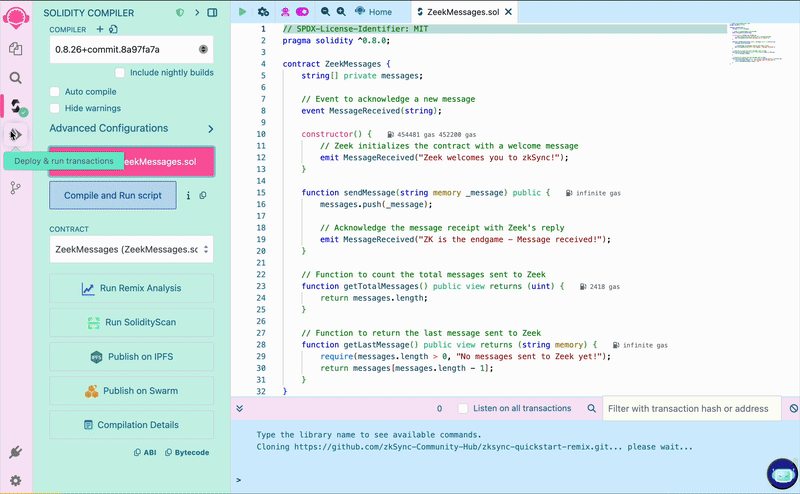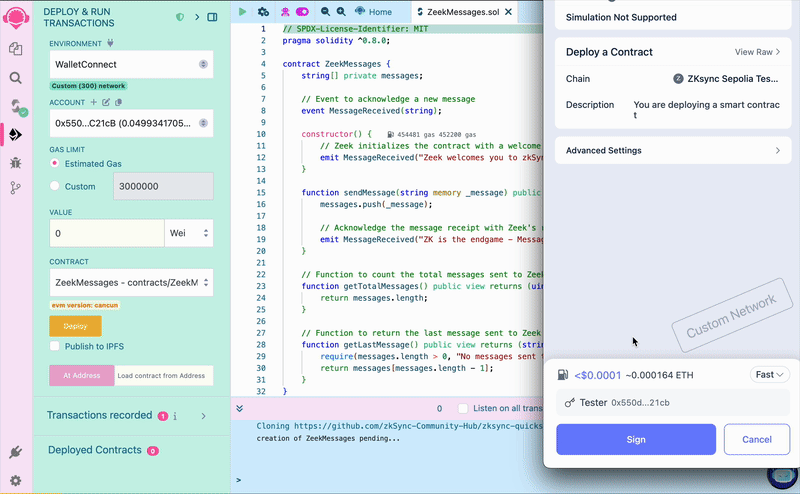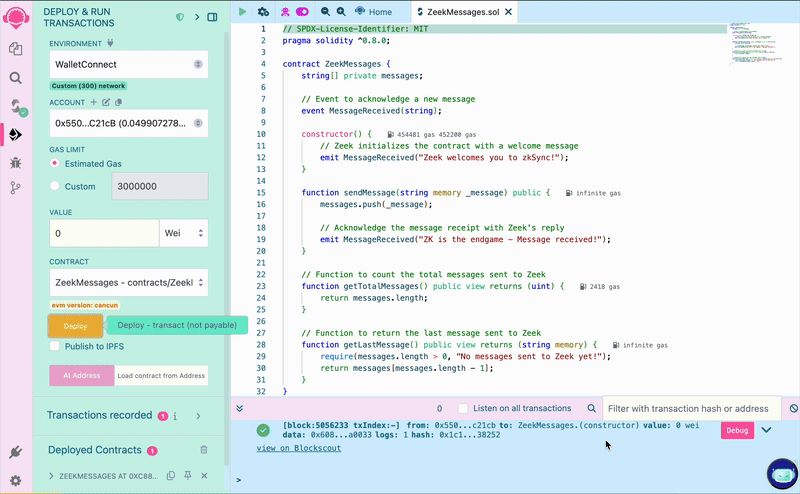
Deploy the contract
To deploy the contract, go back to the "Deploy and run transactions" tab and click on the "Deploy" button. Sign the transaction in your wallet and wait a few seconds until it's processed. Congratulations, you’ve deployed your first contract to ZKsync Sepolia Testnet!
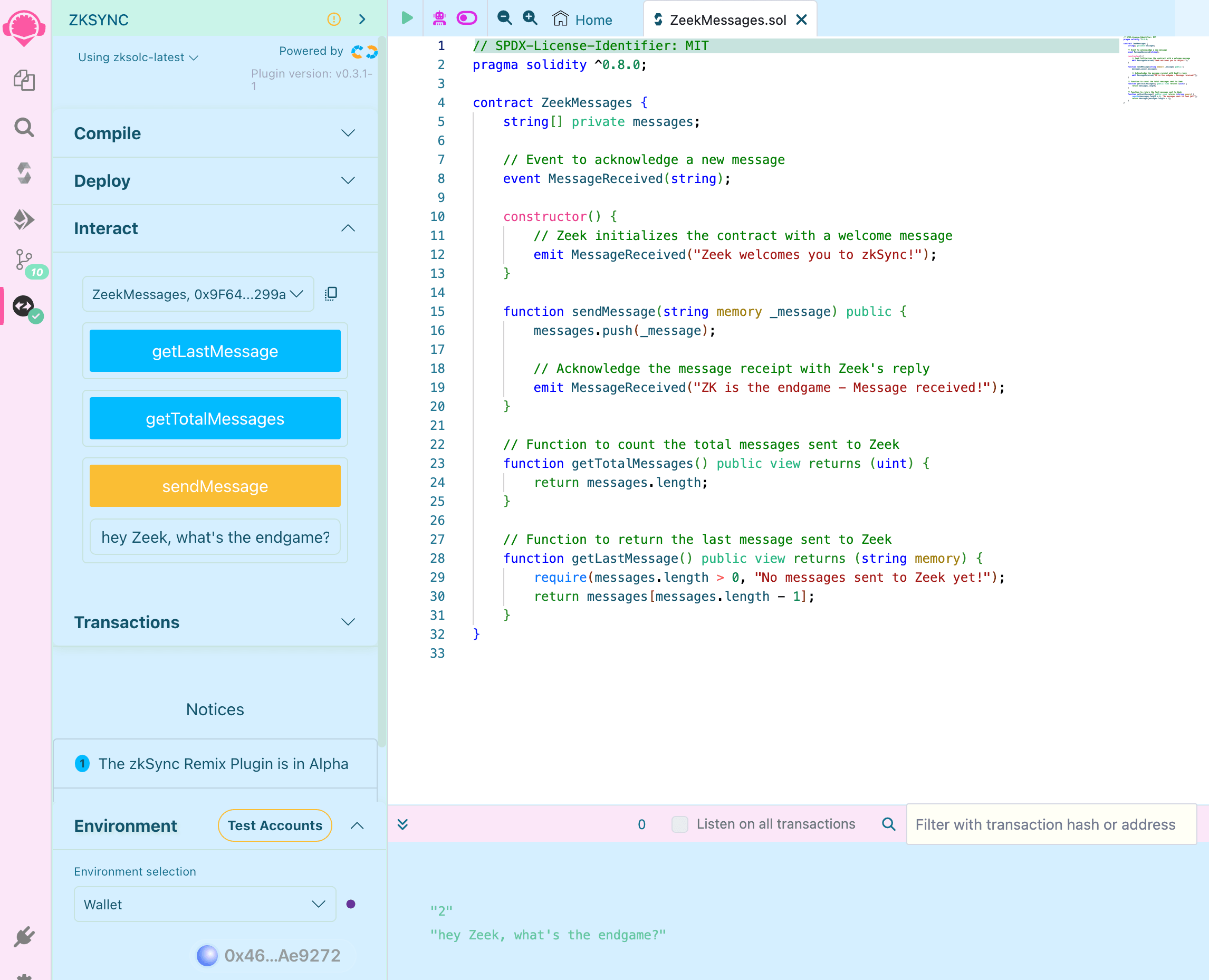
Interact with the contract
Under "Deployed Contracts", click on your contract to show the interaction options:
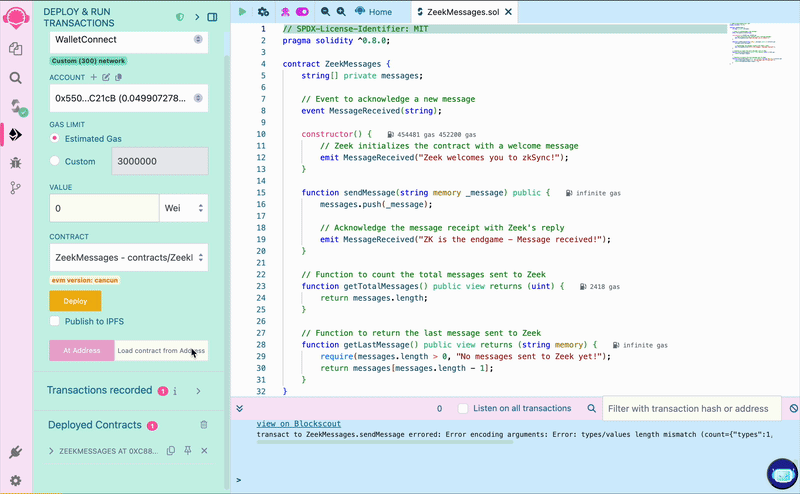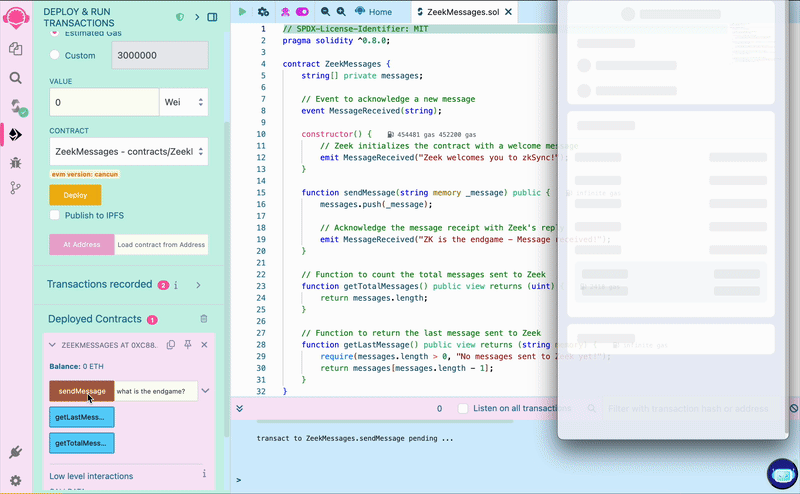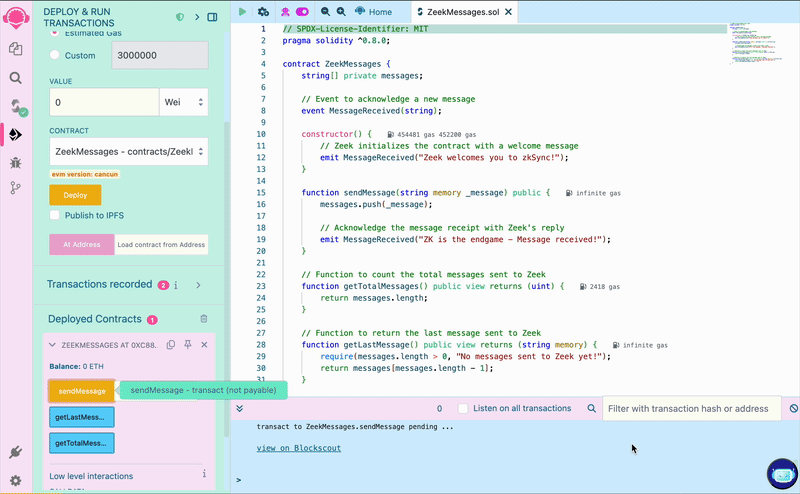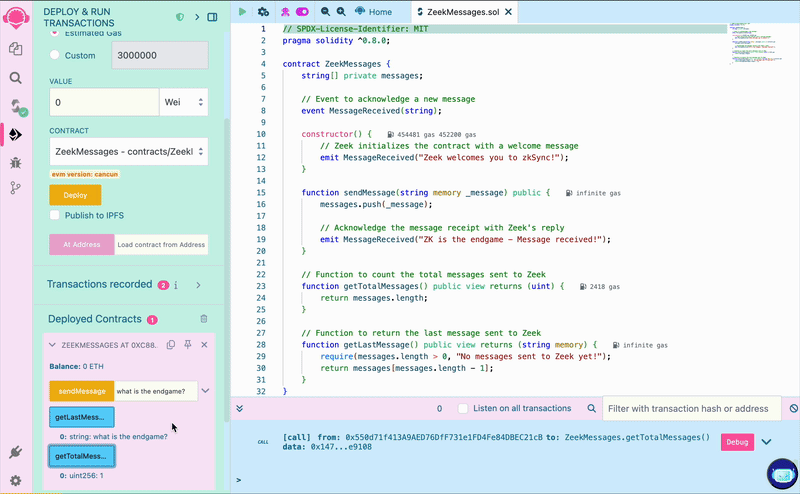
Write a message in the form, click the “sendMessage” button and confirm the transaction in your wallet. Once processed,
click the getTotalMessages and check the response in the terminal, which should be 1. The getLastMessage function
should also return the message you just sent. That means the contract is storing the messages as expected! But how can
we see the replies from Zeek?
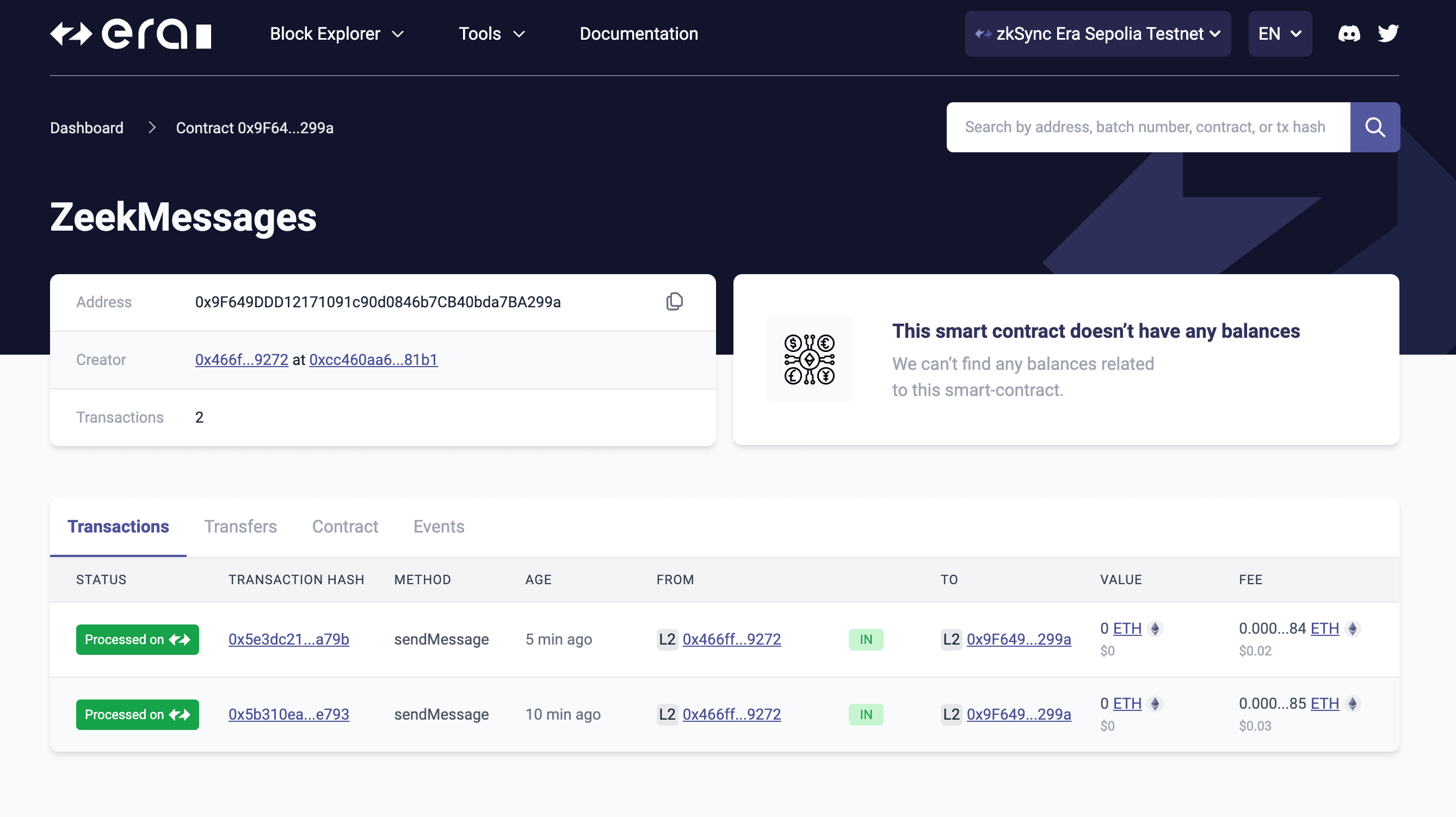
Check the contract in explorer
Copy the smart contract address from Remix and search it via the ZKsync Sepolia Testnet explorer. You’ll see the contract has a transaction from the message you just sent.
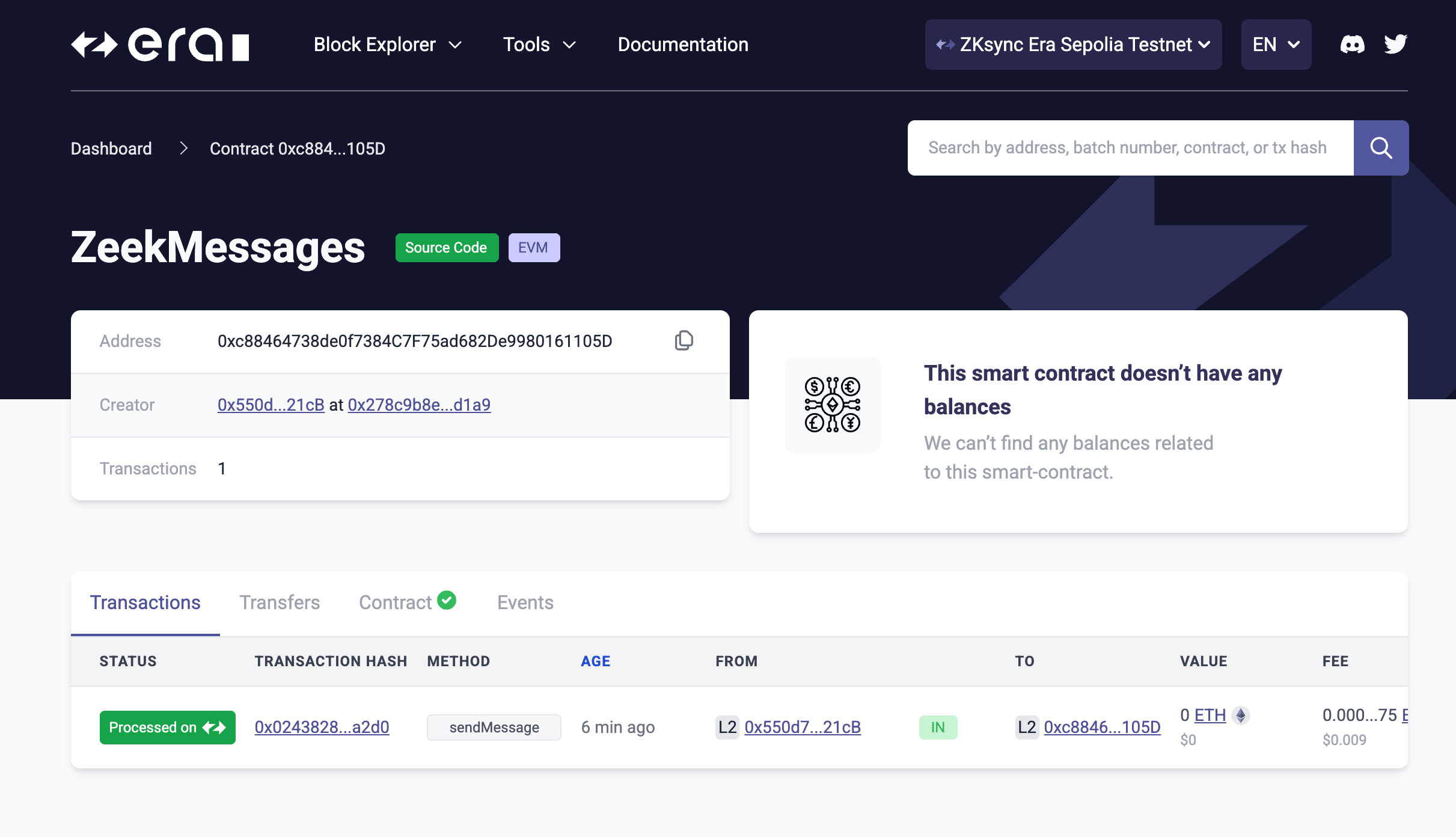
The status will be “Processed” on ZKsync Era and “Sending” on Ethereum. Learn more about the transaction lifecycle on ZKsync.
In the “Contract” tab you’ll see the contract source code as the block explorer automatically partially verified the contract for us.
When a smart contract is verified in a block explorer, it means that the source code of the contract has been published and matched to the compiled version on the blockchain enhancing transparency, as users can review the contract’s source code to understand its functions and intentions.
Finally in the “Events” tab, you’ll see the replies from Zeek as these are emitted as events in our smart contract.
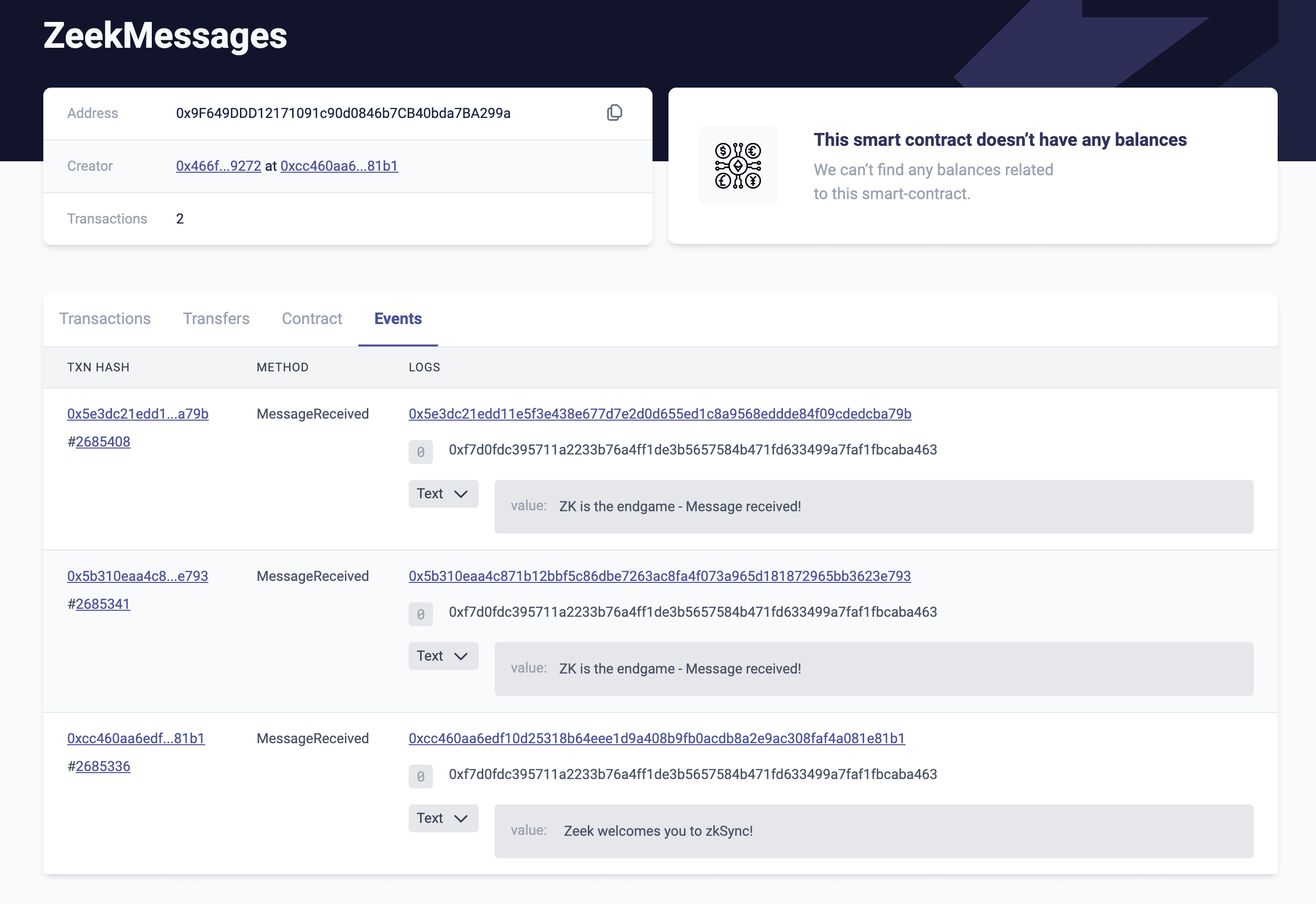
ZK is the endgame ✌️
Takeaways
- EVM-compatibility: ZKsync Era is EVM-compatible and you can write smart contracts in Solidity or Vyper as in Ethereum.
- Custom compilers: smart contracts deployed to ZKsync Era can either be compiled as EVM using default compilers and tools,
or EraVM with the custom compilers:
zksolcfor Solidity andzkvyperfor Vyper. - Browser-based IDEs: You can use existing tools like Remix to deploy EVM or EraVM contracts.
Next steps
- Continue learning by deploying an ERC20 token to ZKsync.
- Join the ZKsync developer community in Discord where you can ask any questions about this
tutorial in the
#dev-quickstartchannel. - Join our GitHub Discussions Community to help other devs building on ZKsync or share your project.